From technological to marketing and social innovations, businesses can leverage various types of innovations to improve their operations, differentiate themselves from their competitors, and meet the evolving needs of their customers. In this article, we will explore the different types of innovations and how they can benefit businesses in different ways. A Guide to Categorizing Types of InnovationInnovation can be classified as a new product, service, or business model that uses either new or existing technology in a new or existing market. It is worth noting that most innovations belong to multiple categories, and the categories often overlap. Therefore, the categorization is intended to provide a framework for analyzing and understanding innovation.
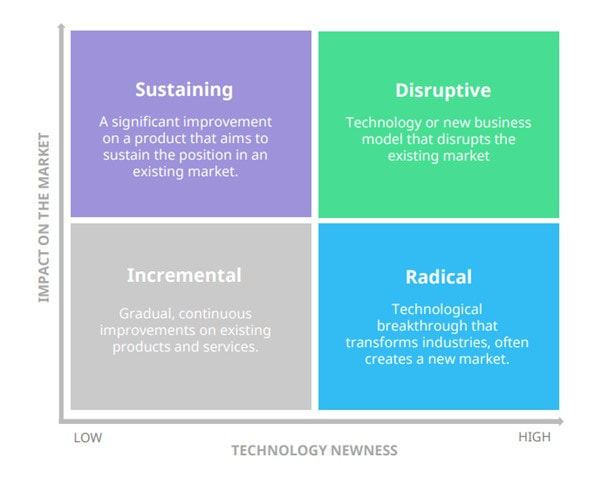
Innovation MatrixThe Innovation Matrix is a tool that categorizes innovation based on two dimensions: the impact it has on the market and the technology it uses. The four categories of innovation in the Innovation Matrix are as follows:
Innovation Matrix Incremental InnovationInnovation is often a continuous and gradual process of improving existing products, services, or concepts in an existing market. Incremental innovation involves making slight improvements to the previous version of a product or service, without drastically changing its core functionality. This can include making products smaller, larger, more attractive, or easier to use, while services can be made more convenient, fast, and efficient for users. Incremental innovation is driven by customer needs and feedback, and can attract higher-paying customers. Some of the key characteristics of incremental innovation include:
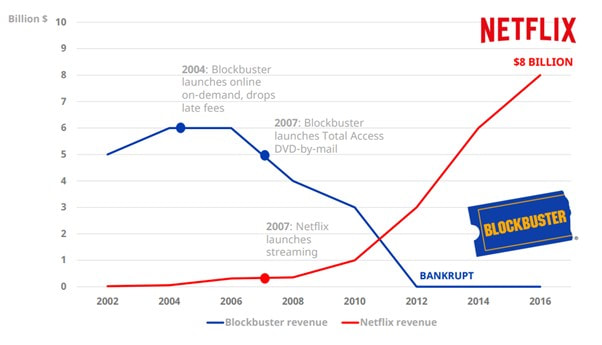
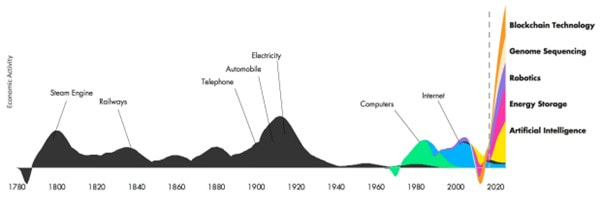
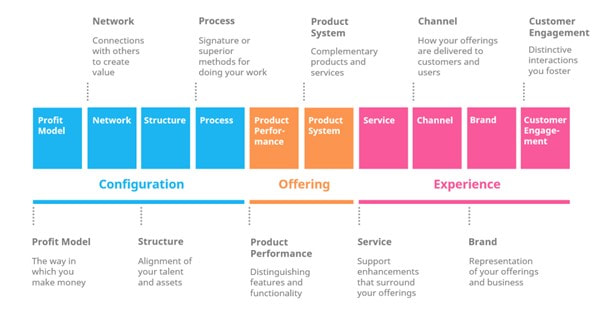
Disruptive InnovationDisruptive innovation, on the other hand, involves the creation of a new value network by entering an existing market or creating a completely new market. It often creates a new market niche and uses new technology or business models. Disruptive innovation involves high risks and initially yields low profits, but if successful, can make traditional business methods uncompetitive. Disruptive innovation does not happen abruptly but rather requires gradual change and a lot of work before reaching the mainstream, where it can have a significant impact on the market. How Disruption Happens Disruptive innovations often have lower performance when measured by traditional value metrics at first, but have other aspects that are valued by a small segment of the market. These types of innovations can turn non-customers into customers but may not appeal to the needs and preferences of mainstream customers yet. Challenges of Disruptive Innovation Established organizations often struggle to adapt to disruptive innovations. They are typically rational when making decisions related to their existing business and fail to adjust to new competition because they are too focused on optimizing their existing offerings or business models that have proven to be successful in the market so far. Once mainstream adoption of disruptive innovation occurs, it may be too late for incumbents to catch up, despite the resources at their disposal. Netflix vs. Blockbuster Netflix is a classic example of a disruptive innovation that uses new technology and a new business model in an existing market, eventually disrupting Blockbuster. Netflix v Blockbuster Sustaining Innovation Sustaining innovation refers to the gradual improvement of a product or service, with each iteration making the product slightly better and reducing defects. This type of innovation targets high-end customers who demand better performance and are willing to pay more for an improved version of the product. Alternatively, the improved product may be cheaper, leading to higher volumes and profits. The iPhone is an example of a sustaining innovation, where newer versions of the phone appeal to the same customer segments and sustain the existing business model in the premium segment of the market. The characteristics of sustaining innovation include a focus on profitable segments, sustaining or improving market position, improving and growing existing value networks, incremental changes, and the risk of being disrupted. Radical InnovationRadical innovation is a rare form of innovation that utilizes revolutionary technology to solve global problems and address needs in completely new ways. This type of innovation can even provide solutions to needs and problems that people didn't know they had, transforming the market or the entire economy. Radical innovation faces significant resistance initially because it is so different from what people are used to. These innovations require a significant amount of time and technological development before they can be adopted by the mainstream. Characteristics of radical innovation include high uncertainty, exploring radically new technology, unprecedented product features, requiring a lot of time and resources, and creating dramatic change that transforms industries. The Future of InnovationAlthough radical innovations are rare, there has been an increasing number of them in recent times. Currently, a new wave of even bigger radical innovations is on the horizon. With the continuous advancement in technology, there is an ever-increasing potential for radical innovation in various industries. Innovators should, therefore, be prepared to embrace these changes to stay relevant and competitive. The future of innovation is bright, and we can expect to see more radical innovations that will transform the world we live in. The Future of Innovation Other Types of InnovationIncremental, disruptive, sustaining, and radical innovations are important concepts to describe the technology and impact of innovation. However, innovation is not limited to these categories. A more pragmatic and holistic approach is required to achieve concrete and actionable results. This section will introduce other types of innovation that can unlock new value in different parts of your business. Doblin’s Ten Types of Innovation Doblin’s Ten Types of Innovation framework is a useful tool for developing viable innovations across all levels of an organization. It is a diagnostic tool that can assess how innovation can be approached internally and which aspects can be improved upon beyond just technological innovation. The framework divides the different types of innovation into three main categories: configuration, offering, and experience, which correspond to business model, product, and marketing in layman terms. It can be used to revisit existing strategies and identify areas for improvement. In addition to Doblin’s framework, there are other types of innovation that can be useful for improving different areas of your business:
By understanding and utilizing these different types of innovation, you can identify new opportunities to create value and drive growth in your business. Doblin’s Ten Types of Innovation The types on the left side of the framework are the most internally focused and distant from customers. As you move toward the right side, the types become increasingly apparent and obvious to end users. Tips for Using the Framework Effectively To effectively use the ten types framework for innovation, consider the following tips:
Product InnovationProduct innovation is a common form of innovation that involves improving the performance characteristics and attributes of a product. It can also involve using components that differ from previously manufactured products. Product innovations can be built using new technologies or by combining existing ones in a new way, though they do not necessarily have to involve technology at all. Product innovation can improve quality and product reliability, giving a competitive edge or helping to sustain market position, while also reducing processing and manufacturing costs. Focus on Product Innovation when:
Service InnovationService innovation involves the creation of a new or significantly improved service concept, product, or process in a new or existing market. It can be a new customer interaction or distribution channel, a system that improves delivery processes, or new solutions in the customer interface. Differentiating a business through service innovation helps respond better to customer needs and expectations, creating more value and generating new revenue streams. A big part of a successful business is the ability to make your customers lives easier and the better you’re able to meet the needs and expectations of the ones you serve, the brighter your future looks like. Service innovation is a great way to:
UberEATS Uber is an example of a company that has used service innovation to create further growth outside of its core business. UberEATS has used Uber's strengths and unique capabilities to enter adjacent markets, such as restaurant and grocery home delivery businesses. Uber’s unique capabilities enable rapid market entry:
Process InnovationProcess innovation refers to implementing a new or significantly improved production or delivery method, using new technologies or improved methods to save time, money, or better serve customers. It may also involve support function processes in HR or finance. Robotic process automation (RPA), for example, is a type of process innovation that uses software with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities to handle high-volume, repeatable tasks that previously required humans. Process Innovation Technology InnovationTechnological innovation is a critical success factor for increased market competitiveness, involving new or improved technology. Incremental innovations improve the existing technology to meet the needs of customers in the existing market, whereas disruptive innovations are game-changers that create a new market. Radical innovations provide solutions that transform the industry, whereas sustaining innovations make gradual improvements to maintain the market position. Technological innovations can be incremental, disruptive, radical or sustaining as follows:
Business Model Innovation Business model innovation involves a fundamental change in how a company delivers or captures value from the market. It includes strategy, resources, capabilities, channels, and values, and often happens through new pricing mechanisms, revenue streams, or distribution channels.
Business model innovation is a fundamental change in how a company delivers value to its customers or captures it from the market. In practice, it often happens through the development of new pricing mechanisms, revenue streams or distribution channels but isn’t limited to them. Signs that indicate that your business is at risk of being disrupted:
iTunes v Spotify Purchasing music, for example, has transformed twice in the past couple of decades. iTunes is an interesting example of disaggregation business model – a strategy that breaks down or separates something into constituent parts or elements. Before iTunes started to sell single tracks, you either had to buy the entire album to hear your favorite song or sit by the radio at the right time to be able to record it. Later, Spotify took the digital music business to a completely different direction with its freemium streaming model by cutting out the middleman and dealing with customers directly online to which Apple now has had to respond with its own Apple Music service. Marketing InnovationMarketing innovation refers to an innovation that brings significant changes to the traditional marketing mix of an industry. Its main objective is to create new markets or increase market share in existing ones. In order for an innovation to be successful, it is essential that people are able to find it and benefit from it. Hence, the ability to connect with customers is crucial and continuous improvement of customer relationships and engagement is necessary. As technology and customer preferences continue to evolve, new marketing innovations are required to promote both new and existing products and services. Innovative marketing practices can help to enhance customer relationships and exceed their expectations. L’Oréal This cosmetics company is a prime example of how technology can be integrated into marketing innovation. The company developed the Makeup Genius App to engage a wider customer group and improve their interaction with the brand. Such innovative technologies not only enhance customer experience but also provide an opportunity to improve the online shopping experience by suggesting products that match the customer's personal preferences. It is important to note that marketing innovations do not necessarily always require new technology to be successful. Architectural InnovationArchitectural innovation, coined by Rebecca Henderson and Kim Clark in 1990, involves the reconfiguration of existing product technologies. The fundamental aspect of architectural innovation is that it changes the relationship between the core components of the product, while the components themselves remain unchanged. This type of innovation deals with the overall design, system, or the interaction of components. One classic example of architectural innovation is the Sony Walkman, which utilized existing components that were previously used in other products. Modular InnovationModular innovation, also known as component innovation, is the opposite of architectural innovation. In modular innovations, one or more components of a product are altered while the overall design remains the same. For instance, a clockwork radio that generates its own electricity and operates for extended periods of time uses the architecture of an established radio but has a unique impact because it can be used in areas with power shortages. Social InnovationSocial innovations are new practices or technological inventions aimed at satisfying social needs better than existing solutions. Public or commercial entities may provide or finance such innovative solutions. While improvement isn't always the result of innovation, some of the critical social outcomes of social innovation are economic growth, enhanced well-being, improved communication, increased educational access, and environmental sustainability from society's perspective. Sustainability and environmental problems such as climate change are challenges that necessitate a lot of effort and innovative solutions now and in the future. Often, policies or other methods are insufficient to effect change, at least not quickly enough. As a result, new, responsible innovative technologies are critical to the long-term survival of our society and nature. Therefore, new green technology solutions, such as eco-friendly vehicles and clean water solutions, will undoubtedly provide numerous benefits in the future. Overall, understanding the different types of innovation and leveraging them effectively can help businesses create new opportunities, generate more revenue, and gain a competitive edge. By considering each type and exploring new ways to configure them, businesses can make significant strides towards innovation and growth. SummaryInnovation is a vital aspect of progress and development, and it has played a significant role in shaping human society throughout history. From simple inventions like the wheel to more complex innovations like the internet, human beings have always strived to improve their lives through innovation. Innovation is not just about creating new products or services; it is also about finding new ways to solve problems, improving processes, and creating value for customers. Today, innovation continues to be a key driver of economic growth, and businesses that prioritize innovation are more likely to succeed and thrive in a rapidly changing marketplace. However, innovation is not always easy, and it requires creativity, risk-taking, and a willingness to experiment and learn from failure. Companies that foster a culture of innovation and invest in research and development are more likely to stay ahead of the curve and stay competitive in the long run. In conclusion, innovation is a crucial aspect of human progress, and it will continue to shape our future in countless ways. Whether it's improving healthcare, advancing technology, or creating new forms of entertainment, innovation has the power to transform our world and create new opportunities for growth and prosperity. By embracing innovation and investing in research and development, individuals and organizations can unlock their full potential and make a positive impact on the world around them.
0 Comments
Each horizon represents a different time frame, risk level, and potential for growth. In this article, we will explore the McKinsey Three Horizons of Growth framework in detail, including its benefits and challenges, the process for applying it, and examples of companies that have successfully used this approach. Each horizon represents a different time frame, risk level, and potential for growth. Lets takes a closer look at each of these horizons. Horizon 1 Horizon 1 represents the core business of the organization and includes its current products, services, and markets. The focus of Horizon 1 opportunities is on optimizing and improving the existing business model, products, and services to maintain competitiveness and profitability. Horizon 1 opportunities may include improving operational efficiency, optimizing pricing strategies, and expanding the customer base. Horizon 2 Horizon 2 represents emerging opportunities that have the potential to become a new source of growth for the organization. These opportunities may involve expanding into new markets, developing new products or services, or creating new business models. Horizon 2 opportunities may require more investment and risk than Horizon 1 opportunities but offer greater potential for growth. The goal of Horizon 2 is to create a pipeline of opportunities that can be developed over time to sustain the organization's growth. Horizon 3 Horizon 3 represents opportunities that are further out in the future, often involving new technologies, markets, or business models that do not yet exist. These opportunities require significant investment and may take longer to develop, but they have the potential to become significant sources of growth in the future. Horizon 3 opportunities may involve exploring new and emerging technologies, developing new business models, or entering entirely new markets. The goal of Horizon 3 is to create a portfolio of options that can be pursued as the organization's core business matures and new opportunities emerge. The McKinsey Three Horizons of Growth framework helps organizations to balance short-term and long-term growth opportunities, prioritize investment in innovation and growth, and allocate resources effectively across different horizons. By evaluating growth opportunities across different horizons, organizations can create a more comprehensive and strategic approach to growth and innovation. Benefits
Challenges
While the McKinsey Three Horizons of Growth framework provides a useful structure for evaluating growth opportunities, it should be used in conjunction with other strategic planning tools to ensure a comprehensive analysis of growth opportunities. The ProcessThe process for applying the McKinsey Three Horizons of Growth framework involves the following steps:
Overall, the McKinsey Three Horizons of Growth framework provides a structured approach to evaluating and prioritizing growth opportunities across different time frames and risk levels, which helps organizations to balance short-term and long-term goals and allocate resources effectively. Alternative ApproachesThere is no one-size-fits-all approach to strategic planning and evaluating growth opportunities, as different organizations have different needs and contexts. While the McKinsey Three Horizons of Growth framework is still widely used and can be effective in many cases, there are other approaches that can also be considered, depending on the specific situation. Here are some other approaches to strategic planning and evaluating growth opportunities that have gained popularity in recent years:
Ultimately, the best approach to strategic planning and evaluating growth opportunities depends on the organization's specific context, resources, and goals. It is important to consider a variety of approaches and tools and tailor them to the specific needs and challenges of the organization. The Framework in Action Here are some examples of companies that have successfully used the McKinsey Three Horizons of Growth framework:
These are just a few examples of how companies have successfully used the McKinsey Three Horizons of Growth framework to balance short-term and long-term growth opportunities and allocate resources effectively. In SummaryThe McKinsey Three Horizons of Growth framework is a useful tool for organizations to categorize and prioritize growth opportunities across different horizons. By evaluating growth opportunities in this way, organizations can balance short-term and long-term goals and allocate resources effectively. The framework encourages organizations to focus on optimizing and improving their current business (Horizon 1), developing emerging opportunities that have the potential for growth (Horizon 2), and exploring new and emerging technologies, markets, or business models that do not yet exist (Horizon 3). While there are pros and cons to using this approach, it remains a popular strategic tool for organizations today. Ultimately, the success of the McKinsey Three Horizons of Growth framework will depend on how effectively organizations apply it to their specific business context and goals. Design thinking involves understanding the needs and perspectives of users, generating and testing ideas, and refining solutions through rapid prototyping and iteration. Originally developed in the context of product design, design thinking has since been applied to a wide range of fields and industries, from healthcare and education to finance and public policy. In this article, we will explore the basics of design thinking, its key principles and practices, and its applications in the enterprise. We will also examine the benefits and challenges of using design thinking, and offer some tips for incorporating it into your organization's innovation process. Whether you are a business leader, designer, or innovator, understanding the principles and practices of design thinking can help you create more customer-centric, effective, and impactful solutions that meet the needs and expectations of users. The Design Thinking ApproachDesign thinking is a problem-solving approach that puts the user at the center of the process. It is a methodical, human-centered approach to innovation that involves empathy, collaboration, experimentation, and iteration. The goal of design thinking is to create solutions that are both desirable for users and feasible for businesses or organizations to implement. The design thinking process typically involves five stages:
Overall, design thinking is a highly collaborative and iterative process that focuses on creating solutions that are both user-centered and practical. It is often used in product design and development, but can be applied to a wide range of fields and industries. Applications for Design Thinking in the EnterpriseDesign thinking has many applications in the enterprise so lets take a closer look at a few examples:
Design thinking can be applied to many different areas within an enterprise, from product development and service design to process improvement and organizational culture. By using a human-centered, iterative approach to problem-solving, organizations can create more effective, efficient, and innovative solutions that meet the needs and expectations of users and stakeholders. Indeed, design thinking has become increasingly popular in enterprises as a way to foster innovation, improve customer experiences, and drive business growth. However, as with any approach or methodology, there are benefits and challenges to using design thinking in the enterprise. Benefits of Design Thinking
Challenges of Design Thinking
Overall, the benefits and challenges of design thinking in the enterprise depend on the specific context and goals of the organization. While there are some challenges and risks associated with design thinking, many organizations have found that it can be a powerful tool for driving innovation and improving customer experiences. Adding Value to Innovation ArchitectureInnovation architecture, which we covered in a previous article, refers to the process and systems that organizations use to manage and drive innovation. It involves creating a framework for generating, evaluating, and implementing ideas, as well as allocating resources and managing risk. Design thinking can complement and add value to innovation architecture in several ways:
Design thinking can complement and add value to innovation architecture by bringing a user-centric and creative mindset to the innovation process. By incorporating design thinking principles and practices into innovation architecture, organizations can generate more innovative and impactful solutions that better meet the needs of users and stakeholders. Tips for Incorporating Design ThinkingHere are some tips for incorporating design thinking into an organization's innovation process:
By incorporating these tips into your organization's innovation process, you can leverage the principles and practices of design thinking to develop more effective, user-centered, and innovative solutions. Remember that design thinking is an ongoing process that requires continuous experimentation, iteration, and learning. With time and practice, you can develop a culture of innovation and creativity that helps drive growth and success for your organization. ConclusionOrganizations develop more effective and innovative solutions. By putting the needs and experiences of users at the center of the design process, organizations can create products, services, and processes that are more intuitive, user-friendly, and impactful. While design thinking can be challenging to implement within an organization, it is worth the effort. By fostering a culture of innovation, encouraging experimentation and collaboration, and using an iterative approach to problem-solving, organizations can create more value for their customers and stakeholders. Design thinking is not a silver bullet, however. It requires ongoing effort, experimentation, and learning to be effective. It also requires leadership buy-in, adequate resources, and a willingness to take risks and learn from failure. Overall, design thinking offers a powerful framework for innovation and problem-solving within organizations. By incorporating its principles and practices into your organization's innovation process, you can develop more effective, user-centered, and innovative solutions that drive growth and success. An effective innovation architecture can help organizations foster a culture of innovation, drive successful new product development, and create sustainable competitive advantage. Innovation architecture can include a variety of elements, such as processes, tools, metrics, and resources, that help to foster a culture of innovation and support the innovation process. An effective innovation architecture should include the following elements:
By building a strong innovation architecture, organizations can improve their ability to generate new ideas, develop and test those ideas quickly and efficiently, and bring successful innovations to market. Frameworks for Innovation ArchitectureThere are several frameworks that can be used for innovation architecture, depending on the needs and context of the organization. Here are some examples:
Overall, the choice of framework will depend on the specific needs and context of the organization, as well as the goals of the innovation initiative. The innovation architect will need to carefully evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of different frameworks to determine which one is best suited to the situation at hand. In the next few sections, we'll explore both 'Design Thinking' and 'Lean Startup'. The Process of Innovation ArchitectureThe process for innovation architecture can vary depending on the organization, the specific challenge or opportunity, and the resources available. However, the following steps are often involved in the innovation architecture process:
Throughout the process, the innovation architect will need to communicate effectively with stakeholders, build and manage teams, and stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in the relevant industry or market. Flexibility and adaptability are also important qualities, as the innovation architecture process often involves navigating uncertainty and navigating complex challenges. Examples of Innovation ArchitectureHere are a few examples of innovation architecture in action:
Overall, these examples illustrate how organizations can use innovation architecture to drive creativity, collaboration, and agility in their innovation initiatives. Let's take a closer look at Google's Innovation Lab. Google's Innovation LabGoogle's innovation lab, also known as Google X, is a secretive research and development lab within Google's parent company, Alphabet. The lab was established in 2010 and is tasked with developing cutting-edge technologies and products that have the potential to change the world. Google X employs a range of innovation architecture frameworks to support its work, including design thinking, agile development, and lean startup principles. The lab's process involves identifying promising new ideas, prototyping and testing them, and then iterating based on feedback and data. One of the hallmarks of Google X is its willingness to tackle ambitious and unconventional projects. The lab is known for taking on projects that may seem far-fetched or impossible, such as self-driving cars, high-altitude balloons that provide internet access to remote areas, and smart contact lenses that can measure glucose levels for people with diabetes. Google X is also known for its culture of experimentation and risk-taking. Employees are encouraged to pursue bold ideas and to take risks in their work, with the understanding that failure is a natural part of the innovation process. Despite the secrecy surrounding Google X's work, the lab has produced a number of successful products and technologies. For example, the self-driving car project has been spun off into a separate company called Waymo, and Project Loon has been used to provide internet access to people in disaster-stricken areas around the world. Overall, Google X is a prime example of how innovation architecture can be used to support breakthrough innovation and create products and technologies that have the potential to change the world. SummaryInnovation architecture is a powerful framework that can help organizations drive innovation and create sustainable competitive advantage. By creating a structured approach to innovation that includes strategy, culture, leadership, processes, tools, and metrics, organizations can improve their ability to generate and implement new ideas. To build a successful innovation architecture, organizations must be willing to embrace risk-taking, experimentation, and continuous learning. They must foster a culture of innovation and provide the resources and support needed to drive innovation forward. By implementing an effective innovation architecture, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their customers, create innovative new products and services, and position themselves for long-term success in the marketplace. In conclusion, innovation architecture is a critical element of modern business strategy, and organizations that embrace it will be better positioned to thrive in an ever-changing and competitive business landscape. |
AuthorTim Hardwick is a Strategy & Transformation Consultant specialising in Technology Strategy & Enterprise Architecture Archives
March 2025
Categories
All
|